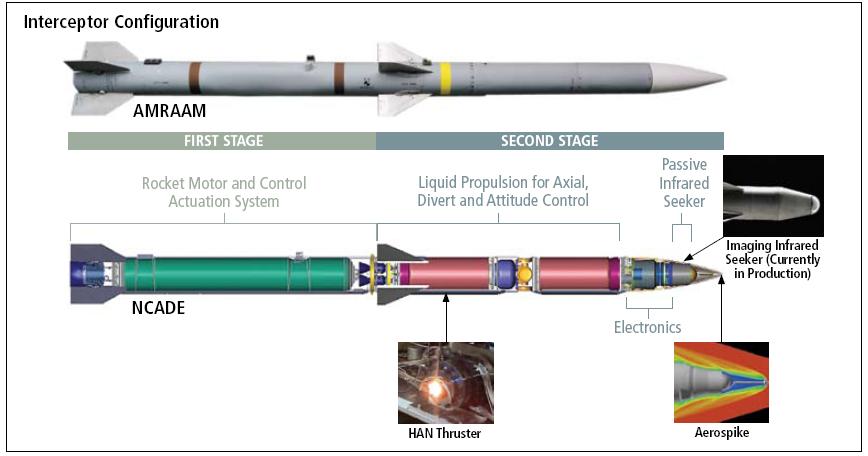
The Network Centric Airborne Defense Element (NCADE) is a small, low-cost, air-launched, anti-ballistic missile developed by Raytheon and Aerojet and builds on the Advanced Medium-Range Air-to-Air Missile (AMRAAM). The NCADE is being designed to intercept short and medium-range ballistic missiles in their ascent- and boost-phase. NCADE and AMRAAM missiles share the same aerodynamic design, aircraft interface and flight control system.
These commonalities enable it to be carried and launched by a wide range of combat aircraft utilized by the United States such as the F-15, F-16, F/A-18, F-22 and F-35. In addition, NCADE’s small size means it could be used by unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) .
One of the key component of the NCADE missile is its advanced infrared (IR) seeker which is able to acquire and track a ballistic missile in its boost phase. In early December 2007, the infrared seeker was successfully tested at White Sands Missile Range mounted on an AIM-9X air-to-air missile which intercepted a surrogate ballistic missile after being launched from an Air National Guard (ANG) F-16 aircraft.
NCADE Specifications
Length: 144 inches
Diameter: 7 inches
Weight: 330 pounds